. What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence is the field of computer science concerned with building intelligent machines or computer systems, capable of simulating human intelligence. The machines created using Artificial Intelligence can work and react like humans without human intervention. Speech Recognition, Customer service, Recommendation Engine, Natural Language Processing (NLP) are some of the applications of Artificial Intelligence.
Since its inception, AI research has explored and rejected a variety of methodologies, including mimicking the brain, modelling human problem-solving, formal logic, massive knowledge libraries, and imitating animal behavior. Highly mathematical-statistical machine learning dominated the subject in the first decades of the twenty-first century. The many sub-fields of AI research are based on specific aims and the application of certain techniques. Reasoning, knowledge representation, planning, learning, natural language processing, sensing, and the ability to move and manipulate objects are all conventional AI research aims. One of the field's long-term goals is general intelligence (the capacity to solve any problem). AI researchers have adapted and integrated a wide range of problem-solving strategies to handle these issues, including search and mathematical optimization, formal logic, artificial neural networks, and statistics, probability, and economics methodologies. AI also makes use of various fields like psychology, linguistics, philosophy.
2. What are some real-life applications of Artificial Intelligence?
- Social Media: The most common use of Artificial Intelligence in social media is facial detection and verification. Artificial Intelligence, along with machine learning, is also used to design your social media feed.
- Personalized online shopping: Shopping sites use AI-powered algorithms to curate the list of buying recommendations for users. They use data like users' search history and recent orders to create a list of suggestions that users might like.
- Agriculture: Technologies, especially Artificial Intelligence embedded systems, help farmers protect their crops from various adversities like weather, weeds, pests, and changing prices.
- Smart cars: Smart cars are another one of the real-life applications of AI. Artificial intelligence collects data from a car’s radar, camera, and GPS to operate the vehicle when the autopilot mode is on.
- Healthcare: Artificial Intelligence has come out as a reliable friend of doctors. From intelligent testing to medical recommendations, they assist medical professionals in every possible way.
3. What are different platforms for Artificial Intelligence (AI) development?
Some different software platforms for AI development are-
- Amazon AI services
- Tensorflow
- Google AI services
- Microsoft Azure AI platform
- Infosys Nia
- IBM Watson
- H2O
- Polyaxon
- PredictionIO
4. What are the programming languages used for Artificial Intelligence?
Python, LISP, Java, C++, R are some of the programming languages used for Artificial Intelligence.
5. What is the future of Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence has affected many humans and almost every industry, and it is expected to continue to do so. Artificial Intelligence has been the main driver of emerging technologies like the Internet of Things, big data, and robotics. AI can harness the power of a massive amount of data and make an optimal decision in a fraction of seconds, which is almost impossible for a normal human. AI is leading areas that are important for mankind such as cancer research, cutting-edge climate change technologies, smart cars, and space exploration. It has taken the center stage of innovation and development of computing, and it is not ceding the stage in the foreseeable future. Artificial Intelligence is going to impact the world more than anything in the history of mankind.
6. What are the types of Artificial Intelligence?
There are seven types of Artificial Intelligence. These are:
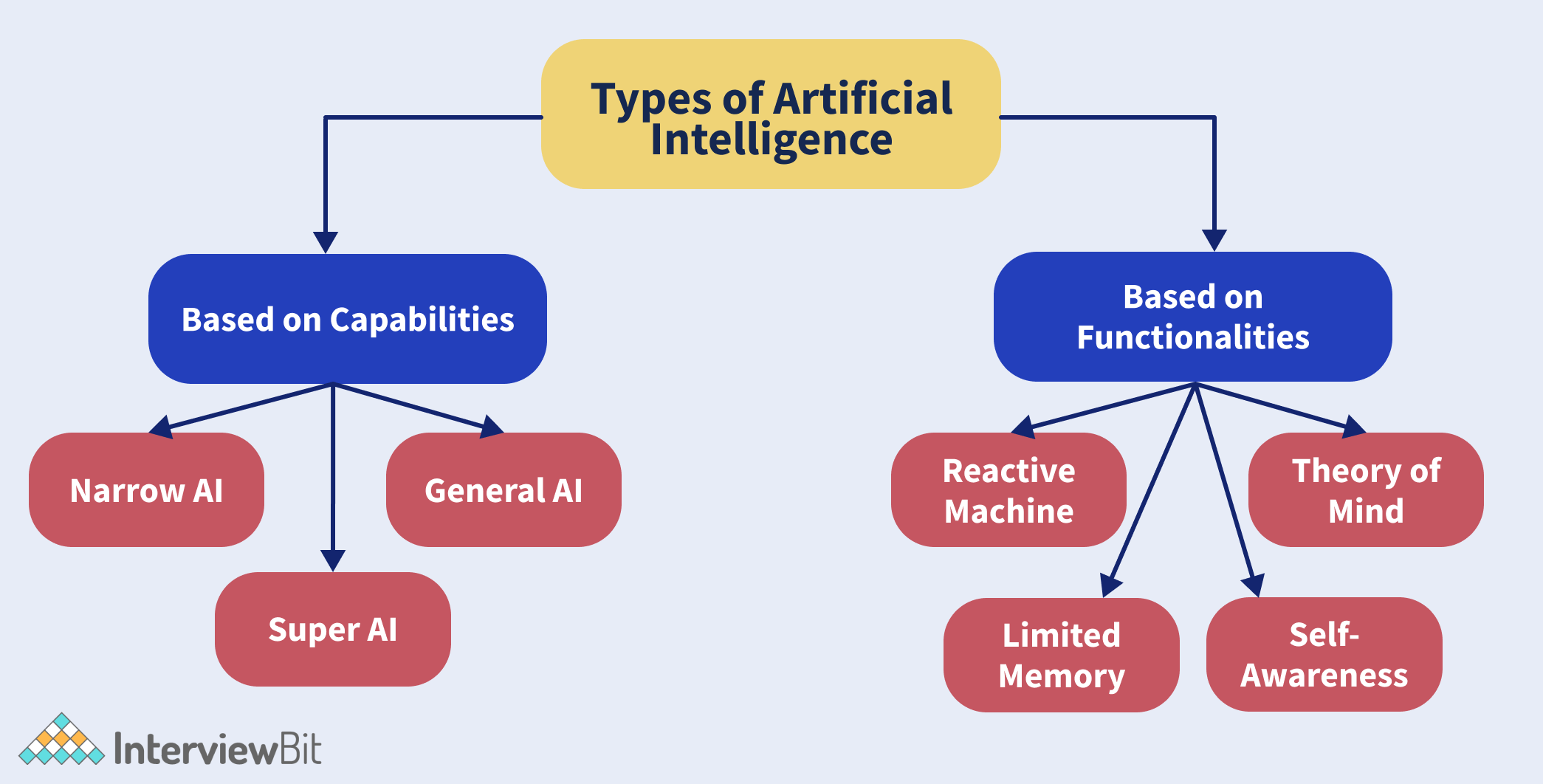
- Weak AI or Narrow AI- These are designed to perform dedicated tasks. They can not perform beyond their capabilities. Apple’s Siri and IBM’s Watson are some examples of weak AI or narrow AI.
- General AI- General AI can perform any intellectual task like humans. Currently, there is no system in the world that can be categorized under general AI. Researchers, however, are focused on developing AI devices that can perform tasks as perfectly as humans.
- Super AI- Super AI is the level of Artificial Intelligence at which it can pass the intelligence of humans and can perform tasks better than humans. Super AI is still a hypothetical concept.
- Reactive Machines- These kinds of machines react in the best possible way in a current situation. They do not store memories or experiences. IBM’s Deep Blue system and Google’s Alpha go are some examples of reactive machines.
- Limited memory- These machines store experiences, but only for a limited amount of time. For example, smart cars store the information of nearby cars, their speed, speed limit, route information for a limited amount of time.
- Theory of mind- The theory of machine AI is a theoretical concept. They might be able to understand human emotions, beliefs, society, and might be able to interact like humans.
- Self-awareness- Self-awareness AI is the future of AI. It is expected that these machines will be super-intelligent, having their own consciousness, emotions, and self-awareness.
7. What is the difference between Artificial Intelligence, Machine learning, and Deep learning?

9. What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of Machine learning, which makes use of artificial neural networks to solve complex problems. The artificial neural network is a concept inspired by information processing and distributed communication nodes, neurons, which are present in human brains. It gives deep learning the power to look at a problem and solve it like a human brain in that situation would. The word ‘deep’ in deep learning means the number of hidden layers in the neural network. Deep learning models are developed in such a way that they are capable of training and managing themselves.
In the above figure, the deep neural network takes input through an input layer. The algorithm's input and output are separated by a hidden layer, in which the function applies weights to the inputs and guides them through an activation function as the output. Activation functions of a Deep neural network may vary. For example, a Sigmoid Function can take any input and produce the output between 0 and 1. The output layer is the network's last layer that takes the information gleaned from the hidden layer and turns it into a final value.
In a nutshell, the hidden layers conduct nonlinear changes on the network's inputs. The function of the neural network determines the hidden layers, and the layers themselves may vary depending on their associated weights.
10. What are different types of Machine Learning?

- Supervised Learning: Supervised learning is the easiest type of machine learning. It is used to train the machine with labeled data. Labeled data is a group of samples that have been tagged with one or more labels (information tags). The labeled data is fed to the machine one by one until the machine can recognize the data on its own. It is just like a teacher trying to teach a kid all kinds of labeled cards in a deck of cards one by one. The data itself is the teacher in supervised learning.
- Unsupervised Learning: Unsupervised learning is, interestingly, the opposite of supervised learning. It is used for data with without labels or information tags. The algorithm is fed with a lot of data and tools to understand the properties of data. The machine will organize the data in clusters, classes, or groups in such a way that it can make sense. Taking a huge amount of random data as an input and making sense out of it is what makes this learning model brilliant.
- Reinforcement learning: The reinforcement learning model from the above-mentioned learning models. It is a kind of model which learns from its mistakes. When we place a reinforcement learning model in any environment, it makes a lot of mistakes. We provide a positive feedback signal when the model performs well and a negative feedback signal when it makes errors, to promote positive learning and make our model efficient.
11. What are the misconceptions about Artificial Intelligence?
Some misconceptions about Artificial Intelligence that exists are:
- Machines learn from themselves- The reality is far from the statement. Machines are not yet at that stage where they can make a decision on their own. Machines learn through a process called machine learning that enables systems to learn and develop based on their experiences without having to be explicitly programmed. Machine learning is concerned with the creation of computer programs that can access data and learn on their own.
- Artificial Intelligence is the same thing as Machine learning- Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning differ from each other. Artificial Intelligence concerns itself with creating devices that can mimic human intelligence, while machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence which is about creating programs that can analyze data, learn from it, and then make decisions.
- Artificial Intelligence will take over humans- There is a possibility that the capabilities of AI can match or even surpass human intelligence in the near future. But, saying that AI will take over humans is just a work of fiction. AI is supposed to complement human intelligence, not enslave it.
Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions for Experienced
12. What is Q-learning?
Q Learning is a model-free learning policy that chooses the best course of action in an environment, depending on where in the environment the agent is (an agent is an entity that makes a decision and enables AI to be put into action). Model-free learning policy means that the nature and predictions of the environment to learn and move forward. It does not reward a system to learn, it uses the trial and error method instead.
The model's goal is to determine the optimum course of action given the current situation. To accomplish this, it may devise its own set of rules or act outside of the policy that has been established for it to obey. This means there isn't a real need for a policy, which is why it's called off-policy. The agent's experience is saved in the Q table in Q-learning, and the value in the table indicates the long-term reward value of executing a certain action in a specific condition. The Q learning algorithm, according to the Q table, can instruct the Q agent the action to take in a given situation to maximize the predicted reward
What is the difference between a strong AI and a weak AI?
| Strong AI | Weak AI |
|---|---|
| Strong AI is a theoretical form of AI with a view that machines can develop consciousness and cognitive abilities equal to humans. | Weak AI, also called narrow AI, is AI with limited functionality. It refers to building machines with complex algorithms to accomplish complex problem-solving, but it does not show the entire range of human cognitive capabilities. |
| Strong AI can perform a wide range of functions. | In comparison to strong AI, weak AI has fewer functions. Weak AI is unable of achieving self-awareness or demonstrating the full spectrum of human cognitive capacities and operate within a pre-defined range of functions. |
| Strong AI-powered machines have a mind of their own, and they can think and accomplish tasks on their own. | Weak AI-powered machines do not have a mind of their own. |
| No machine of strong AI exists in reality. | Examples include Siri or Google Assistant. |

Comments
Post a Comment