Breadth First Search or BFS for a Graph
Breadth First Search or BFS for a Graph
Breadth First Traversal (or Search) for a graph is similar to Breadth First Traversal of a tree (See method 2 of this post). The only catch here is, unlike trees, graphs may contain cycles, so we may come to the same node again. To avoid processing a node more than once, we use a boolean visited array. For simplicity, it is assumed that all vertices are reachable from the starting vertex.
For example, in the following graph, we start traversal from vertex 2. When we come to vertex 0, we look for all adjacent vertices of it. 2 is also an adjacent vertex of 0. If we don’t mark visited vertices, then 2 will be processed again and it will become a non-terminating process. A Breadth First Traversal of the following graph is 2, 0, 3, 1.
For example, in the following graph, we start traversal from vertex 2. When we come to vertex 0, we look for all adjacent vertices of it. 2 is also an adjacent vertex of 0. If we don’t mark visited vertices, then 2 will be processed again and it will become a non-terminating process. A Breadth First Traversal of the following graph is 2, 0, 3, 1.
Following are the implementations of simple Breadth First Traversal from a given source.
The implementation uses adjacency list representation of graphs. STL‘s list container is used to store lists of adjacent nodes and queue of nodes needed for BFS traversal.
Output:
Following is Breadth First Traversal (starting from vertex 2) 2 0 3 1
Illustration :
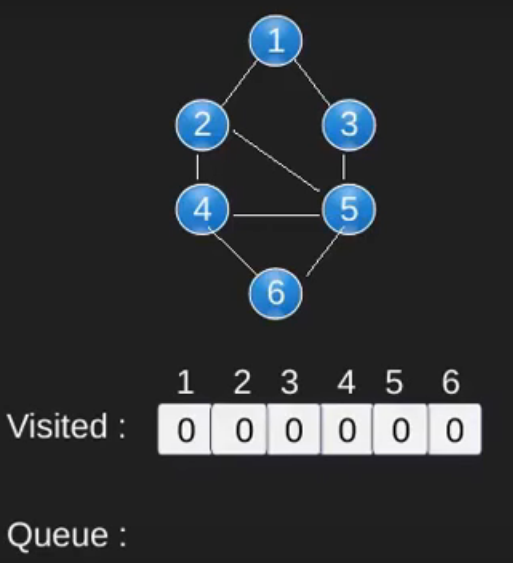
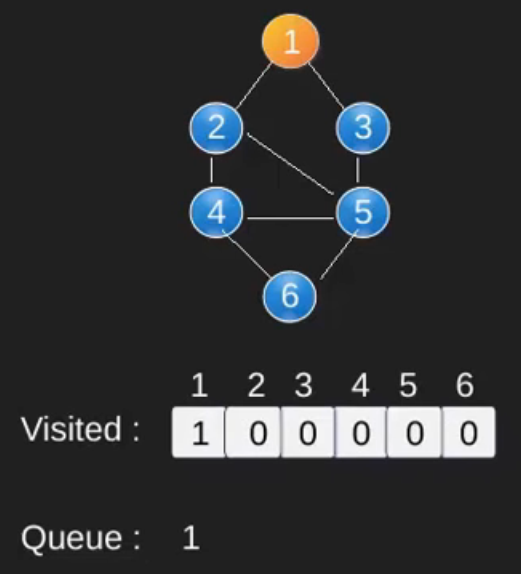
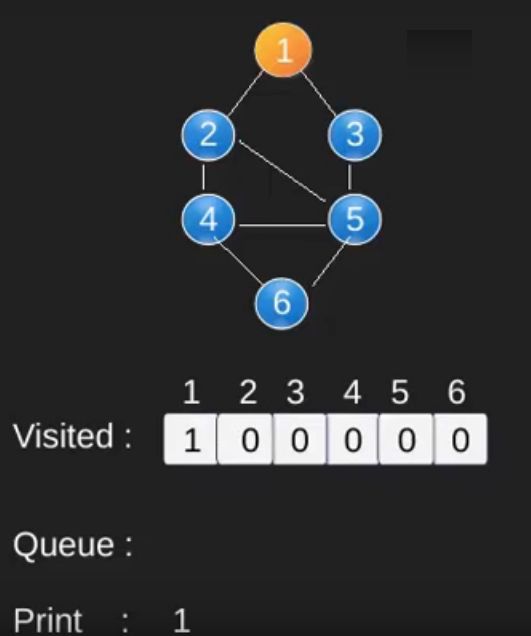
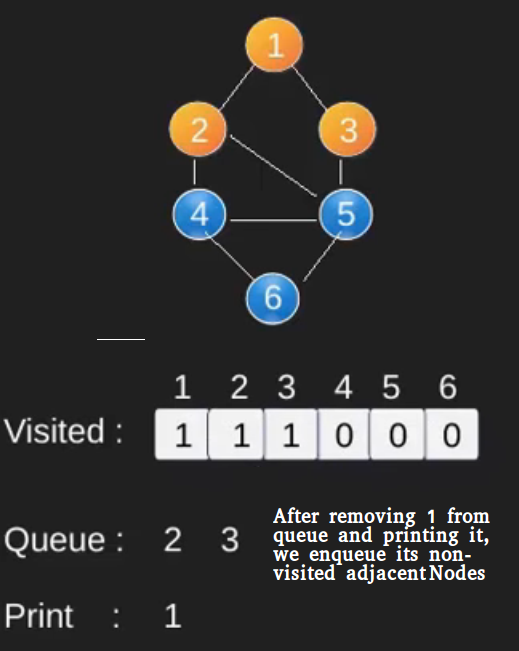
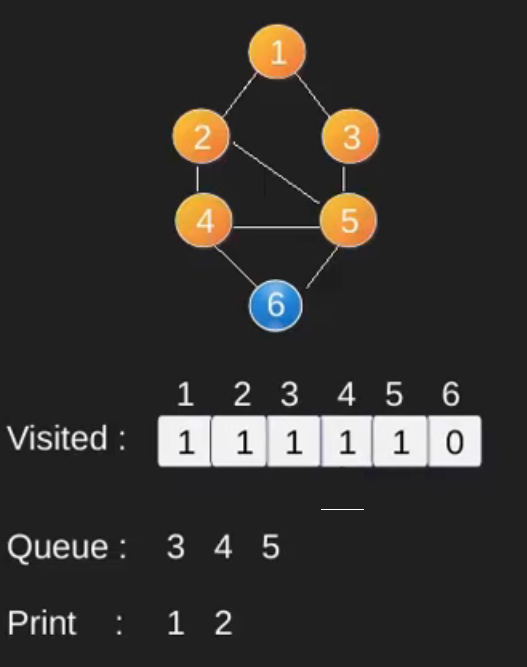
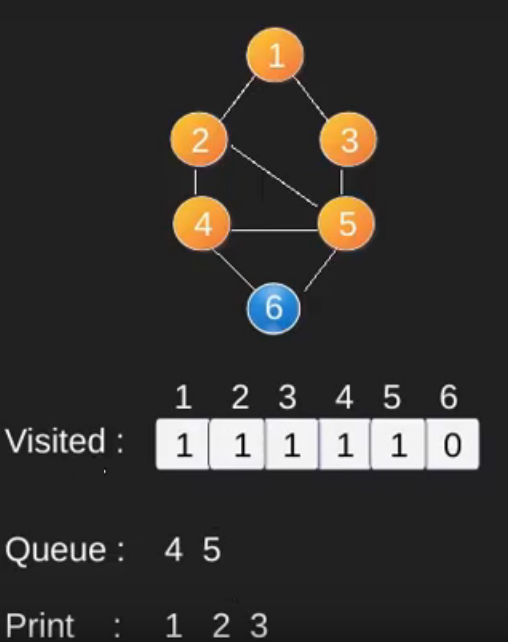
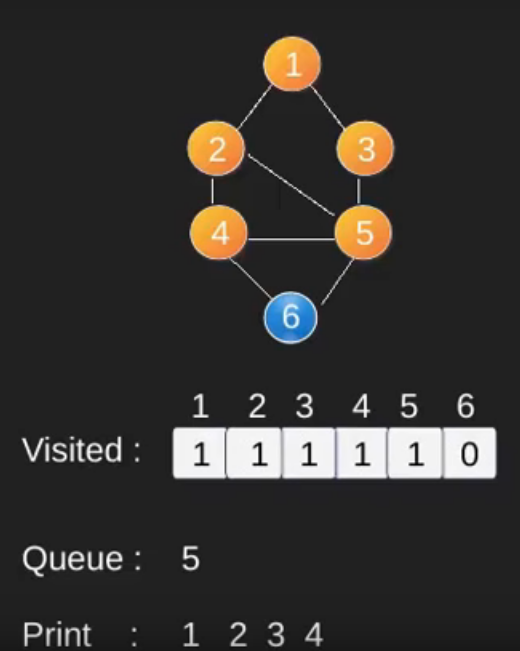
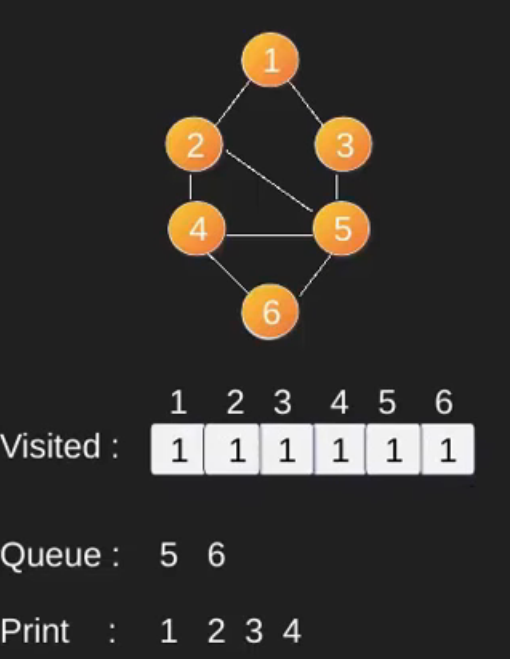
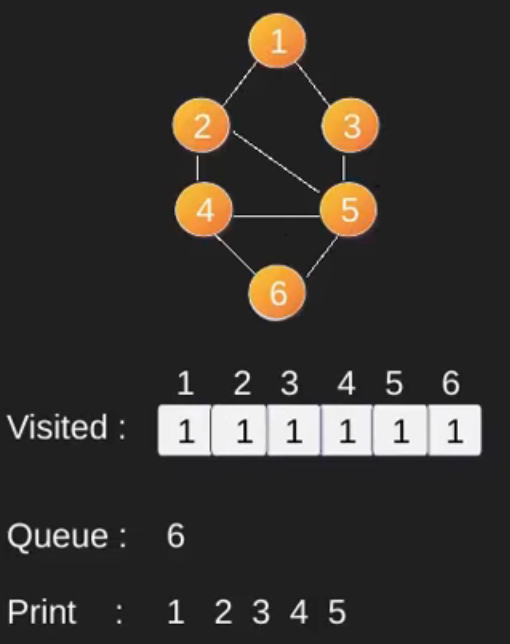
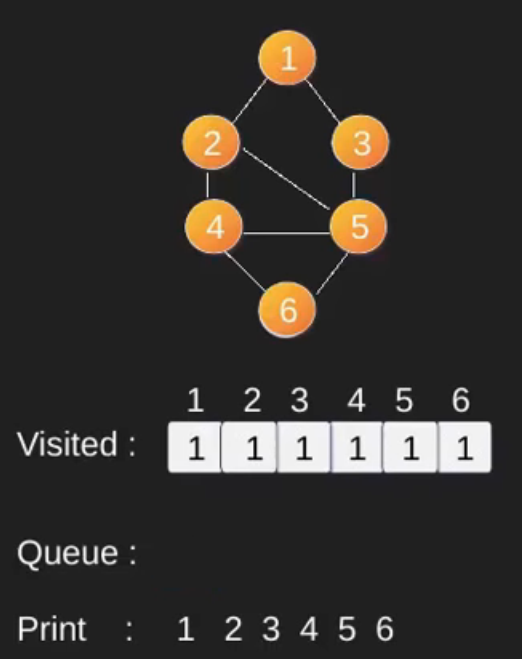










Note that the above code traverses only the vertices reachable from a given source vertex. All the vertices may not be reachable from a given vertex (example Disconnected graph). To print all the vertices, we can modify the BFS function to do traversal starting from all nodes one by one (Like the DFS modified version) .
Time Complexity: O(V+E) where V is number of vertices in the graph and E is number of edges in the graph.

Comments
Post a Comment